Dyslipidemia is a condition in which the levels of bad cholesterol (LDL) are high and the levels of good cholesterol (HDL) are low. The disease is usually inherited but can also be caused by a genetic mutation. The most common inherited form is heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia, which causes increased LDL and high HDL cholesterol. Although children with dyslipidemia are unlikely to have symptoms, those with this disorder should see a doctor to get a diagnosis.
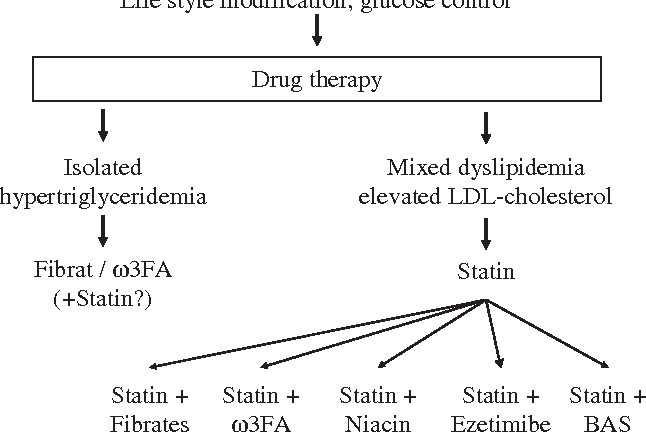
In most cases, doctors focus on lowering the levels of triglycerides and LDL. The treatment for dyslipidemia depends on the cause and severity of the condition. In severe cases, physicians may prescribe a lipid-modifying drug, such as a statin. These drugs block the production of cholesterol in the liver. Some people with hyperlipidemia may require the use of prescription medications. For those with a mild case, dietary changes are sufficient, while those with severe cases may require statins.
If you’re suffering from dyslipidemia, it’s vital to see a doctor as soon as possible. The treatment will depend on the cause of your disease and how severe it is. If you have high levels of LDL cholesterol, your doctor may prescribe a lipid-modifying drug to lower your levels. This drug will interfere with the production of cholesterol in the liver. If you have high levels of LDL, your physician may recommend a statin or other medication.
The treatment for dyslipidemia is primarily focused on lowering LDL and triglycerides. However, treatment depends on the underlying cause and severity of your condition. In most cases, doctors prescribe lipid-modifying drugs. For people with high levels of LDL, this medication works by blocking the enzymes responsible for making cholesterol in the liver. Patients with high levels of LDL cholesterol will usually require treatment with statins or another lipid-modifying drug.
In addition to the risk of cardiovascular disease, high levels of LDL and HDL cholesterol are associated with hyperlipidemia. As a result, these disorders can lead to heart disease, stroke, and diabetes. The treatment for dyslipidemia includes lifestyle changes to lower LDL cholesterol and increase HDL. It is important to maintain a healthy lifestyle. As a result, the triglycerides and LDL cholesterol levels of your blood are optimal.
People with high levels of triglycerides may be at increased risk of heart disease, especially if they have a family history of it. Other risk factors for dyslipidemia include tobacco use and diet. Symptoms of dyslipidemia can be mild or severe and may not require treatment. For some patients, dyslipidemia is a chronic condition that requires ongoing monitoring. If you are at a high-risk level of triglycerides, your doctor will prescribe medications that can help your cholesterol levels remain stable.
If you are concerned about high triglycerides, you should consult your doctor. It is important to note that dyslipidemia and hyperglycemia are not the same. Both conditions involve high levels of LDL cholesterol and triglycerides. Inheritance is the most common cause of high LDL and triglyceride levels in people with familial combined hyperlipidemia. Those with this condition are at greater risk for developing early coronary artery disease.
The causes of dyslipidemia are varied. Typically, it can be caused by tobacco use, physical inactivity, diet, or obesity. For patients with type 2 diabetes, it is important to define secondary and primary prevention strategies. For example, a patient with familial hypercholesterolemia should change their diet and exercise. But in some cases, there is no specific cause for dyslipidemia. Patients with type 2 diabetes are advised to change their diet to reduce their risk of the disease and their cholesterol levels.
If you have hyperlipidemia, you should contact https://sagg2019.com/
immediately. It is important to treat dyslipidemia if it causes swelling of the heart or if you have diabetes. Your doctor will monitor your cholesterol levels to determine what treatment is needed. The first step is to improve your diet. You should eat plenty of fruits and vegetables and avoid trans fats. Also, you need to get enough sleep. Quality sleep can significantly affect the risk of cardiovascular disease.
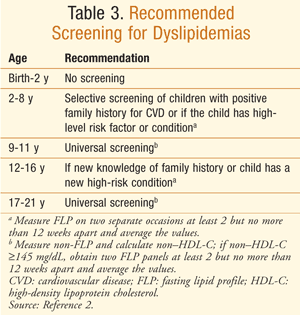
The recommended cholesterol level for children is 190 mg/dl to 280 mg/dl. A high concentration of LDL is considered a higher risk. An elevated HDL level is considered lower. A healthy person with low HDL levels has a lower risk of heart disease. The doctor may need to take statins. As a rule, these medicines are not suitable for young children. If your child has dyslipidemia, it is best to visit a pediatrician. Your doctor will check your LDL and HDL levels to make sure they are within acceptable limits.