Cervical cancer is a condition affecting both women and men. It is most common in women between the ages of 35 and 44, but older women are also at risk. If they have not been getting regular screenings, they are at an increased risk of developing the condition. There are several types of cervical cancer, including squamous cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma, and mixed carcinoma. Both types can be deadly, so it is important to get checked for early detection and treatment.
Cervical cancer usually starts when DNA changes appear in healthy cells in the cervix that turn off a gene called a tumor suppressor. These genes keep cells under control and cause them to die at the right time. However, genetic mutations can turn oncogenes and turn off tumor suppressor genes. This process is called "switching". Human papillomaviruses are known to alter the p53 and Rb genes, resulting in a cancerous mass.
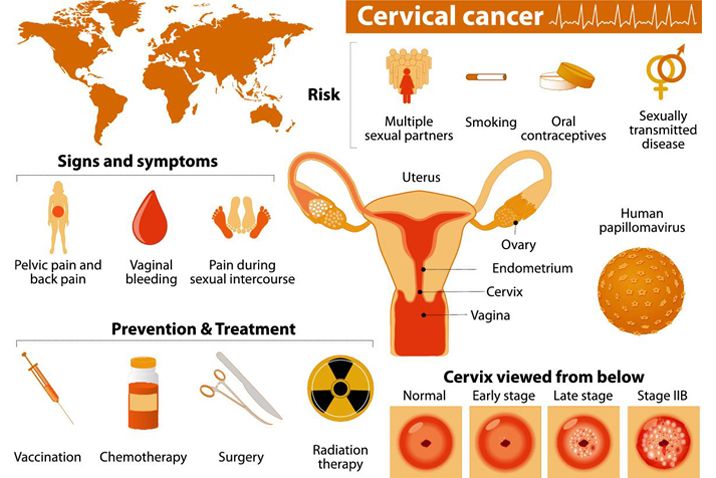
Symptoms of cervical cancer may include pain in the vagina or pelvic area. Usually cervical neoplasms are harmless. The risk of developing this disease in women is less than one percent. In rare cases, cancer cells can spread to the lungs, liver, bones, and other organs. A Pap smear is often the first step in diagnosing the disease. A Pap smear is a test that collects cells from the cervix and checks for precancerous changes.
If you are experiencing any of the symptoms mentioned above, you may have cervical cancer. In most cases, the diagnosis of cervical cancer is made with a screening test or Pap smear. This test can be done at any age. It will also detect precancerous changes in cells that are a sign of the disease. He will determine if you need to be tested or treated. The health website https://www.somosmass99.com.mx/ says that if you have a low-risk cervical tumor, you may not need treatment unless the tumor is very large.
If you are at risk for cervical cancer, it is important to get the vaccine first to prevent the disease. Vaccinations are very effective in preventing this disease. Most women who receive this vaccine do not develop cancer. If you had received the vaccine, you would have been at a higher risk of cervical neoplasia. If you have a precancerous condition, it is recommended to get vaccinated.
If you have cervical neoplasma, you should seek medical care immediately. This cancer can spread to other parts of the body, such as the lungs and the pelvis. It can even block the ureters, which carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder. To find out if you have cervical neoplasma in the first place, you should go to a doctor to get a Pap smear.
A weakened immune system is another cause of cervical neoplasma. The use of immunosuppressive medications may increase your risk of developing cervical cancer. Long-term use of birth control pills also increases the risk. Other risk factors include poor socioeconomic status and HIV. For cervical neoplasma, there are three main causes: infections, aging, and papillomaviruses. There are several ways in which this type of cancer develops.
Some people are at risk for cervical cancer. Infections can cause inflammation and can affect different parts of the body. Infections can also lead to cervical neoplasma. HPV can also lead to cancer. Infections can lead to the spread of HIV and papillomavirus. The virus can cause many types of neoplasmas in women. If you have a virus, it may cause you to develop the disease.
The first step in preventing cervical neoplasmasis is getting vaccinated. The vaccine is a preventative measure against HPV, which causes cervical cancer. There are also many treatments for cervical neoplasmasis. Surgery is the most common method of treatment and involves removing the entire cervix and other pelvic organs. Radiation is another form of treatment for this disease. It destroys cancer cells with high-energy X-ray beams. These beams can be delivered by a metal tube or machine outside the body.
Besides surgical removal of the cancer, chemotherapy may also involve external or internal radiotherapy. External radiotherapy is performed with a machine that uses an x-ray to target the cancer. Internal radiotherapy, on the other hand, uses a smaller device to insert radioactive applicators into the vagina. This method is usually administered to women with cervical cancer. Some women also experience bleeding after menopause. If you are experiencing these symptoms, it is important to visit your doctor.