There are many different tuberculosis types. In the United Kingdom, the average incidence rate was nine cases per 100,000 people, and the highest incidence rate was in Portugal, at twenty cases per 100,000 people. One example is an Egyptian mummy, with evidence of tubercular decay in the spine. The disease was discovered by Robert Koch, who isolated the bacterium responsible for the disease. The infection is not contagious, but the bacteria can be spread to others.
The bacterium that causes tuberculosis can infect the lungs and spread through the air. Bacteria live inside the alveolar air sacs of the lungs, and macrophages try to destroy them by phagocytosis. A membrane-bound vesicle called a phagosome then combines with a lysosome to form a phagolysosome. The bacterium does not die from the phagosome, but survives and multiplies inside the macrophage, which leads to a virulent disease.
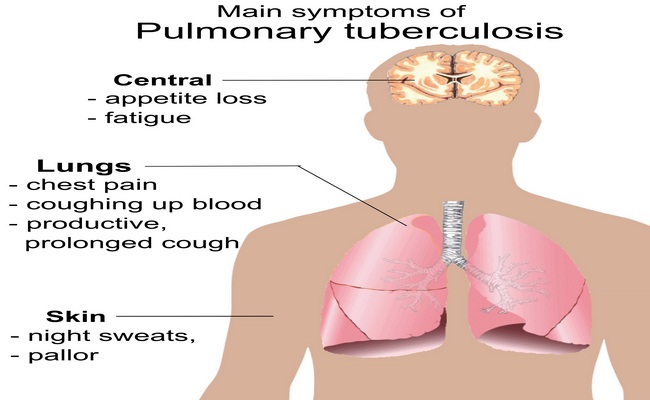
Tuberculosis is an infectious disease that affects the lungs, causing pain and inflammation. It can also affect the joints, causing arthritis and joint damage. Symptoms of the disease can include back pain and stiffness, and bacterial infection can lead to meningitis, which can lead to long-term headaches. Other common side effects of TB include liver and kidney failure, fluid accumulation, and cardiac tamponade, which can be fatal.
Another form of tuberculosis is cystitis, which causes pus in the urine and a burning sensation. When this happens, the infection is atypical and there are no signs of bacteria. A urine culture will not reveal any evidence of the bacterium. This infection can lead to side pain, frequent urination, and general malaise. Therefore, it is important to make a correct diagnosis in order to prevent further complications.
Tuberculous arthritis is another type of tuberculosis. The infection affects the joints, most often the knee and hip. Symptoms of tuberculous arthritis include severe joint pain, fever, and heavy night sweats. A person with tuberculous arthritis may also have a chronic cough. There are many other symptoms of tuberculous arthritis that you can find on the site Raja Changer, but not all of them are necessarily related to the lungs.
TB disease is an infectious disease that can affect the lungs, kidneys, and blood. The most common form is pulmonary tuberculosis, while extrapulmonary TB affects different parts of the body, including the gastrointestinal tract. Although TB is a contagious disease, it does not spread easily between people. Despite the fact that it is highly contagious, most cases of tuberculosis do not cause symptoms.
TB arthritis can affect any joint. In the lungs, it affects the knee and hip joints. It can cause pain, restricted mobility, and low-grade fever. Unlike other types of arthritis, TB arthritis is often mistaken for a simple form of arthritis. However, it can also affect the gastrointestinal tract, including the food pipe. Besides, it can cause ulcers in the stomach and generalized fatigue.
The most common type of tuberculosis is pulmonary tuberculosis, which affects the lungs. Almost two-thirds of cases occur in the lungs. About 20% of the disease occurs in other organs. A tuberculosis vaccine is available commercially, but it is not completely effective. It is best to seek medical treatment if you suspect that you have TB.
TB is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which can be transmitted through a person’s exhaled droplets. TB is highly contagious, and is spread in the same way as flu and colds, but it’s not as contagious as these illnesses. TB is generally transmitted by prolonged contact with another person and is most likely to be transmitted among family members unless a tuberculosis patient is infected by a weakened immune system.
TB can be a life-threatening disease. Fortunately, it can be easily treated. The symptoms of TB vary according to the type of tuberculosis. During the initial stages of the disease, the patient may have no symptoms or have only minor signs and discomfort. Further tests are needed to determine whether the symptoms of TB are due to the presence of antibodies to the bacteria. If the presence of TB is detected in the lung, the bacterium may have already begun to spread throughout the body, which may be harmful to the patient.
Among the tuberculosis types, the most common is the latent form, which is not contagious but can be passed from one person to another. Patients with this type of infection should not have close contact with anyone with the disease. In addition, healthcare workers and visitors to hospitals should follow strict guidelines to protect themselves against the bacteria. They should also avoid direct contact with infected individuals. They should not be exposed to the bacteria of TB.